Click here to download Brochure and click here for further details on Real Estate Track.
Students who wish to enrol in the Economics Honours Programme must complete the Senior Thesis course. To apply for the Senior Thesis course, students must obtain at least B+ in ECON350 Research Methods in Economics, maintain a GPA of at least 3.40 in the Economics Core and Elective courses, and have completed at least 24 course units.
Senior Thesis
The Senior Thesis is a 1-term course which is equivalent to 1 course unit. It includes a presentation of the research paper supervised by a faculty member in the School who is an expert in the relevant research area and examined by an Examiner, who is another faculty member in SMU, together with the Supervisor.
In order to receive Honours in the Economics Major, a student must obtain a grade of at least B in the Senior Thesis course, and maintain a GPA of at least 3.40 in the Economics Core and Elective courses.
Quantitative Economics Track

The Quantitative Economics Track (QET) is designed to respond to the increasing demand from industry, government and academia for graduates with the knowledge and skills required for technical analyses of economic situations and issues. This track is ideal for students who are interested in
- becoming professional economists in the government or private sectors;
- pursuing a more technical career path in industry;
- pursuing graduate studies in Economics or in Finance;
or simply increasing the scope and depth of their knowledge in the quantitative aspects of Economics.
The track requirements are as follows:
- Intermediate Econometrics
- Advanced Microeconomics
- Advanced Macroeconomics
In addition, students need to take 2 elective courses from the following list:
- International Trade
- International Macroeconomics
- Math. Methods for Economic Dynamics
- Empirical Industrial Economics
- Time Series Econometrics
- Research Methods in Economics
Real Estate Track
The Real Estate Track (RET) is designed to provide the students doing Economics and/or Finance majors the opportunity to widen and deepen their knowledge and understanding of real estate. Students will be able to leverage the fundamentals of Economics and/or Finance and acquire the quantitative and qualitative tools necessary for a variety of roles in the sector, such as real estate development, advisory, research, leasing, financing, property/project management, Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITS) management, investment banking, consulting and agency management.
The track aims to develop a pipeline of graduates who will be equipped with a strong grounding in real estate investments and finance. They will be exposed to real estate development in Singapore and the region. The track fits in well with the national objective to develop more talent and skillsets needed to advance Singapore as a hub for real estate financing for the region and participate in China’s “One Belt One Road” initiatives.

The track is complemented with exposure to real-world business practices, case studies and experiential learning opportunities, such as speaker events, local and overseas internships, as well as local and overseas study trips. In addition, bond-free Academic Award will be offered to students.
The RET requires a minimum of 5 courses in Real Estate:
- Real Estate Investments and Finance
- Real Estate Economics
- Risk and Regulations in Real Estate
- Minimum 2 electives from a specified set of courses relevant to the real estate industry
What will this second major do for you?
The objective of the second major is to produce work-ready graduates who are valuable for administration and management of the healthcare sector. Through the courses offered in the second major, the students will be equipped with the knowledge and skills that are necessary for identifying and solving the challenges that the sector is facing or is going to face. The knowledge and skills are reinforced by the first-hand experience in the healthcare sector through internships and experiential learning. This second major will open the door to meaningful career paths in the healthcare industry and is suitable for those with a passion for promoting health and well-being, delivering quality healthcare, contributing to the saving of lives, and ensuring the graceful ageing of society.
Structure & Curriculum
To fulfil the requirements of a second major in HEM, students must complete the following:

Introductory Data Analytics in Healthcare

Health Economics

Health Systems and Policy

Healthcare Management

Economics of Ageing

Financial Accounting

Health Law and Medical Ethics or Medical Law and Health Policy

Health Psychology

Medical Sociology

Operations and Supply Chain Management in Healthcare

Smart Healthcare in Asia

Epidemics: Biomedicine and Global Health

Applied Healthcare Analytics

Medicine and the Law

Intelligent Systems: AI-Driven Healthcare and Social Media Insights

Work Study Elective (2 Course Units)
Related Materials
What will this second major do for you?
ACS equips you to:
- Manage risks with models
Actuarial Science applies rigorous probability and actuarial models to the analysis and management of various risks in organisations, especially insurance companies. - Contribute to the society
By analysing and managing risks, actuaries bring financial security to customers, organizations and the society. - Apply statistical and machine learning methods
Constructing statistical models that generalize data-sets is a powerful quantitative skill. Learning machine learning algorithms that generate predictive models gains additional insight in prediction. - Sharpen your competitive edge
Actuarial Science students have much opportunity for gaining exposure to industry with practical working experience and building good connections through 20-24 weeks internship. - Join a vibrant community
All Actuarial Science students are members of the Actuarial Science Club at SMU. - Pursue the professional designation
The ACS curriculum fulfills all the objectives listed under the Society of Actuaries’ (SOA) Validation by Educational Experience (VEE) guideline. The curriculum also provides actuarial training and prepares you in pursuing the Associate of the Society of Actuaries (ASA). - Have a professional career
Qualified actuary is a well-respected professional who receives world-wide recognition and rewards.



Structure & Curriculum
The ACS curriculum has a requisite of COR2100 Economics and Society and the following ten module requirements:
ACS Courses Requirement

Probability Theory and Applications (STAT201)

Financial Mathematics (STAT203)

Life Contingent Risks (STAT310)

Risk Theory and Loss Models (STAT311)

Statistical Inference for Data Science (DSA201)

Statistical Learning with R (DSA211)*

Financial Accounting (ACCT101/111)

Finance (FNCE101)

Any two DSA3XX Electives
* Statistical Learning with R is mutually exclusive with Statistical Programming, which is a compulsory Accounting Core course for BAcc students. BAcc students can therefore, take Statistical Programming instead of Statistical Learning with R to fulfil their Actuarial Science Second Major requirement.
Industry Integration (II) Track Requirements
A new Industry Integration (II) Track is established in the ACS programme for students who are eager to pursue their professional careers in the actuarial field after graduation. The II Track ensures that ACS students in this track have a higher exposure to industry, better connections, and more practical working experience, as compared to other ACS students not in the track.

ACS students in II Track need to fulfil all ten module requirements, including DSA301 Time Series Data Analysis plus one additional Actuarial Science Work-Study Elective (ACS WSE). ACS students can only declare II Track in ACS programme if they successfully sign up for ACS WSE.
Related Materials
- View the image gallery of the AIA-SMU MOU Signing Ceremony Photos
- Read the article about the AIA-SMU MOU Signing Ceremony
- Download the ACS flyer
- Download the ACS information session slides
- Read the article about the SMU-FIS collaboration to teach Insurance Risk Suite modeling software to our students. More details here.
What Can This Second Major Do for You?
DSA enables you to:
- Turn Data into Insights
Companies are collecting more data than ever. The most successful ones are those that can extract value from it. As a result, data scientists and analysts are in high demand. - Learn Essential Data Skills in Industry-Relevant Languages
Gain hands-on experience in Python, R, and SQL. Learn how to query databases, build data pipelines, create interactive visualizations using JavaScript libraries, and more. - Explore Statistical Learning
Training and testing statistical models that describe and generalize datasets is a powerful tool. Learn how to apply statistical models and machine learning algorithms to generate predictions and uncover insights. - Sharpen Your Competitive Edge
Acquire in-demand data science and analytics skills, including big data and big compute technologies such as Apache Cassandra and Apache Spark. - Apply Your Skills in Real-World Projects
Develop your ability to communicate analysis results to stakeholders. Share your thought process using GitHub and GitHub Pages. Build a portfolio of projects to showcase in internship and job interviews. - Join a Vibrant Community
As a DSA Second Major student, you will be supported by the DSA Society at SMU, a network of peers passionate about data science.



Structure & Curriculum
To fulfil the requirements of the DSA major, students must complete the following:

Probability Theory and Applications (STAT201)

Statistical Inference for Data Science (DSA201)

Statistical Learning with R (DSA211) *

Data Analytics with R (DSA212)

Computational Thinking and Programming (COR-IS1704) **
* Statistical Learning with R is mutually exclusive with Statistical Programming, which is a compulsory Accounting Core course for BAcc students. BAcc students can therefore take Statistical Programming instead of Statistical Learning with R to fulfil the requirements.
** Computational Thinking and Programming is also a Core Curriculum course under the Capabilities (Modes of Thinking) basket. Students may not double count this course towards both the Core Curriculum and the DSA Second Major. Therefore, students must complete (a) an alternative course to fulfil the Capabilities (Modes of Thinking) basket requirement of the Core Curriculum or (b) an extra DSA Second Major Elective. As Computational Thinking and Programming is a compulsory Core Curriculum course under the Capabilities (Modes of Thinking) basket for BSc (CL), BSc (IS) and BSc (SE) students, these students are required to complete 5 CUs of DSA Second Major Electives instead of 4 CUs.
Choose any four courses in the Data Analysis (DA) List and Computing Technology (CT) List, with at least one course in each list.
DA List

Time Series Data Analysis (DSA301) or Economic Forecasting (ECON233)

Spatial Data Analysis – SMU-X (DSA303)

Panel Data Analysis (DSA305)

Big Data Analytics (DSA306) or Big Data Analytics with Spark (DSA307)

Applied Healthcare Analytics (ECON245)

Marketing Analytics (MKTG228) or Service and Operations Analytics (OPIM326) or Forecasting and Forensic Analytics (ACCT420)

SQL and NoSQL Databases (DSA308)

Machine Learning with Applications in Economics (DSA311)

Data Science with Python (DSA312)
CT List

Modeling and Data Analytics (COR1305) or Data Management (IS112) or Business Data Management (IS105)

Visual Analytics for Business Intelligence (IS.428) or Geospatial Analytics and Applications (IS415)

Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (CS420)

Principles of Machine Learning (CS421) or Machine Learning and Applications (IS460)

Data Mining and Business Analytics (IS424) or Data Warehousing and Business Analytics (IS417)

Text Mining and Language Processing (IS450)

Reinforcement Learning in Portfolio Optimisation (QF210)
Related Materials
Alumni Testimonials

In today’s world, complex problems can no longer be solved using a single approach. That is why more and more disciplines complement one another. At the School of Economics, students may be eligible to opt for the double degree programme or complete a second major, providing them with much more flexibility in their career options.
Double Degrees
The double degree programme provides students with added flexibility in their career options. Under the double degree programme, a student can graduate with two degrees in
Economics and Accountancy
Economics and Business Management
Economics and Computer Science
Economics and Computing & Law
Economics and Information Systems
Economics and Social Sciences
Economics and Law (Law must be the primary degree)
Second Majors
Students may choose a second major within the School of Economics, in Actuarial Science, Data Science and Analytics or Health Economics and Management, or select a second major from one of the other Schools.
Examples of second majors:
Accounting
Actuarial Science
Communication Management
Data Science and Analytics
Finance
Health Economics and Management
Information Systems
Legal Studies
Marketing
Organisational Behaviour and Human Resources
Political Science
Psychology
Sociology
Second Major in Economics
Non-BSc (Econ) students may opt to do a second major in Economics
Structure & Curriculum
To fulfill the requirements of the second major in Economics, students must complete the following courses:
Economics Second Major Core Courses
Mathematics for Economics
Microeconomics 1
Macroeconomics 1
Introduction to Econometrics
Economics Second Major Electives
Students are required to complete a minimum of 4 course units of Economics Electives. These must include at least 2 course units from the following:
Economics of Globalisation or Economic Globalisation and Asia
Economic Development in Asia
Microeconomics 2
Macroeconomics 2
International Economics
International Trade
International Macroeconomics
What is Economics?
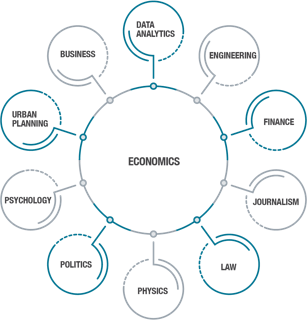
Economics is a science concerned with human behaviour and it intersects many areas of study and application such as Business, Data Analytics, Engineering, Finance, Journalism, Law, Physics, Politics, Psychology, Sociology and Urban Planning.
Economics is about solving problems and improving people’s lives. In this respect it is very relevant to tomorrow’s world and it opens broad career opportunities: from policy making to consulting and running your own company.
Studying economics also provides a hedge in our digital revolution era. With the radically improved computation infrastructure and the availability of big data, the discipline has changed. A core part of the training of an economist focuses on the ability to use these data. Such a skill will help companies and decision makers in making better decisions.
Curriculum for students admitted AY2019-20 onwards
The Bachelor of Science (Economics) programme comprises three key sections: (1) the Core Curriculum, which helps students cultivate a stable intellectual core, cutting across disciplines; (2) the Major Requirements, which help students develop depth in their chosen discipline of study; and (3) the Free Electives, which afford students choice for flexible self-directed learning, towards greater disciplinary depth or multidisciplinary breadth.
Core Curriculum
The first pillar, Capabilities, is about imparting to students the necessary skills to dexterously operate in an increasingly digitised and data-driven working environment. These skills will be imparted in courses from five baskets.
Managing (2 Course Units)
Choose two from:
- Accounting for Entrepreneurs
- Business, Government and Society
- Capital Markets in China
- Leadership and Team Building
- Management Communication
- Spreadsheet Modelling and Analytics
Modes of Thinking (1 Course Unit)
Choose one from:
- Critical Thinking in the Real World
- Computational Thinking
- Managing in a Volatile, Uncertain, Complex and Ambiguous Context
Numeracy (1 Course Unit)
- Calculus
Writing and Reasoning (1 Course Unit)
- Programme in Writing and Reasoning
Internship (1 Course Unit)
The Communities pillar aims to help students understand the economic, technological, and cultural systems that structure our interactions with our communities. It comprises four baskets:
Economics and Society (1 Course Unit)
Technology and Society (1 Course Unit)
Choose one from:
- Can Machines Think? AI in History, Philosophy, and Fiction
- Climate Change: Global and Local Solutions
- Climate, History and Society
- Digital Cultures
- Innovations for Asia’s Smart Cities
- Science, Environment and Empire
- Science and Technology Studies: Where Science meets Society
- Technology and World Change
- Technological Innovations Enhancing Urban Sustainability
- Technological Solutions to Urban Challenges
Cultures of the Modern World (1 Course Unit)
Choose one from:
- Constitutions, Cultures, and Context
- Contemporary South Asian Societies
- Film in Southeast Asia
- Global and Transnational Sociology
- Jurisprudence: Modern and Critical Theories of Law
- Politics of South East Asia
- Singapore: Imagining The Next Fifty Years
- Sustainable Cities
- Understanding China’s Economics Miracles
- Urban Cultures
- Foreign Languages, such as Bahasa Melayu, French, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Mandarin, Spanish, Thai
Community Service (1 Course Unit)
The Civilisations pillar immerses students in the fundamental debates that cut across time and space, preparing them to engage in critical dialogue between multiple and competing traditions of thought and problem-solving.
Ethics and Social/Corporate Responsibility (1 Course Unit)
- Ethics and Corporate Responsibility
Big Questions (1 Course Unit)
Global Exposure
Economics Core and Electives
The Economics Core lays a broad foundation for the study of economics.
Students are required to complete the following courses:
- Introduction to Statistical Theory
- Mathematics for Economics
- Microeconomics 1
- Microeconomics 2
- Macroeconomics 1
- Macroeconomics 2
- Introduction to Econometrics
- Economic Development in Asia
Students are also required to complete one of the following options:
- International Economics; or
- International Trade and International Macroeconomics
Economics Electives provide students with specialised knowledge in various fields of economics. A total of 6 course units must be completed if students read International Economics, or 5 course units if they read International Trade and International Macroeconomics.
The set of Economics Electives is a rich menu of courses offering a wide range of topics to choose from. Some examples are
- Advanced Macroeconomics
- Advanced Microeconomics
- Data Science with R
- Development Economics
- Economic Forecasting
- Economics of Ageing
- Family and the Society: Economic Theories and Practices
- Game Theory
- Health Economics
- Healthcare Management
- Industrial Organisation
- Intermediate Econometrics
- Introductory Data Analytics in Healthcare
- Labour Economics
- Macroeconomics of Income Distribution
- Public Sector Economics
- Real Estate Economics
- Statistical Inference for Data Science
- Statistical Learning with R
- Strategic Thinking
- Urban Economics and Policy
A total of 9 course units must be completed. Free Electives encourage students to take any courses to broaden their knowledge in fields beyond their primary major.
Students may take any SMU course (including Economics Electives) to fulfil this component.
Additional Graduation Requirements
The Digital Technology/ Data Analytics graduation requirement acknowledges the pivotal role that digital technology and data analytics play in today's workplace. By fulfilling this graduation requirement, students will acquire essential skills and knowledge relevant in the digital age.
Sustainability is a pressing global concern. The Sustainability graduation requirement will equip students with an intermediate understanding of sustainability issues, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Singapore is a vibrate global hub and Asia is a region of immense significance in today's global economy. The Singapore and Asia Studies graduation requirement ensures that students gain a strong understanding of the dynamics of Singapore and the Asia region.
Global traction and understanding underpins success in careers in today's globally connected environment. To have global exposure from the vantage of a University education is invaluable for international networking and global vision; it also opens doors to bigger opportunities.




